Tutorial
- Selecting an analysis module
- Analyzing user-provided data
- Analyzing preloaded data
- Setting parameters
- Submitting your job
- Demo
- Output
SurvNet is a valuable bioinformatic tool for identifying network-based biomarkers that most correlate with patient survival data. The web app takes three input files: one network file as the searching platform; one molecular profiling file (e.g., microarray gene expression data or methylation data); and one patient survival data file. SurvNet will automatically search for subnetworks that most correlate with patient survival data and display the results in a visually appealing way.
Selecting an analysis module
[top]To run SurvNet, you have three options:
- Analyze Your Data, which is to identify network-based biomarkers in user-provided datasets
- Analyze Preloaded Data, which enables users to explore preloaded, multidimensional TCGA molecular data.
- Analyze a set of sample data (no user-provided input files are required).

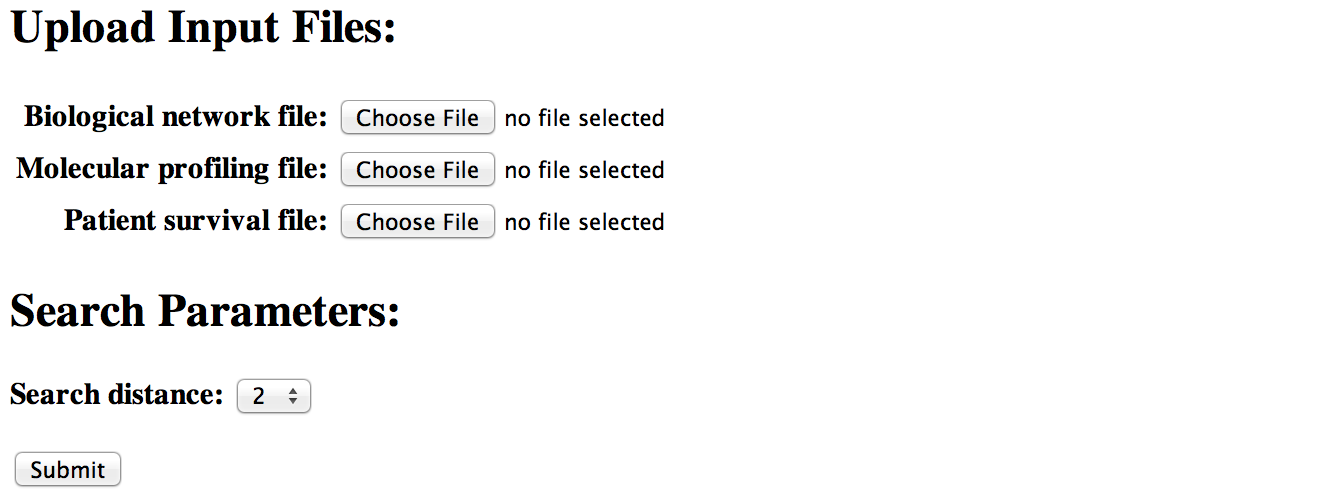
Analyzing user-provided data
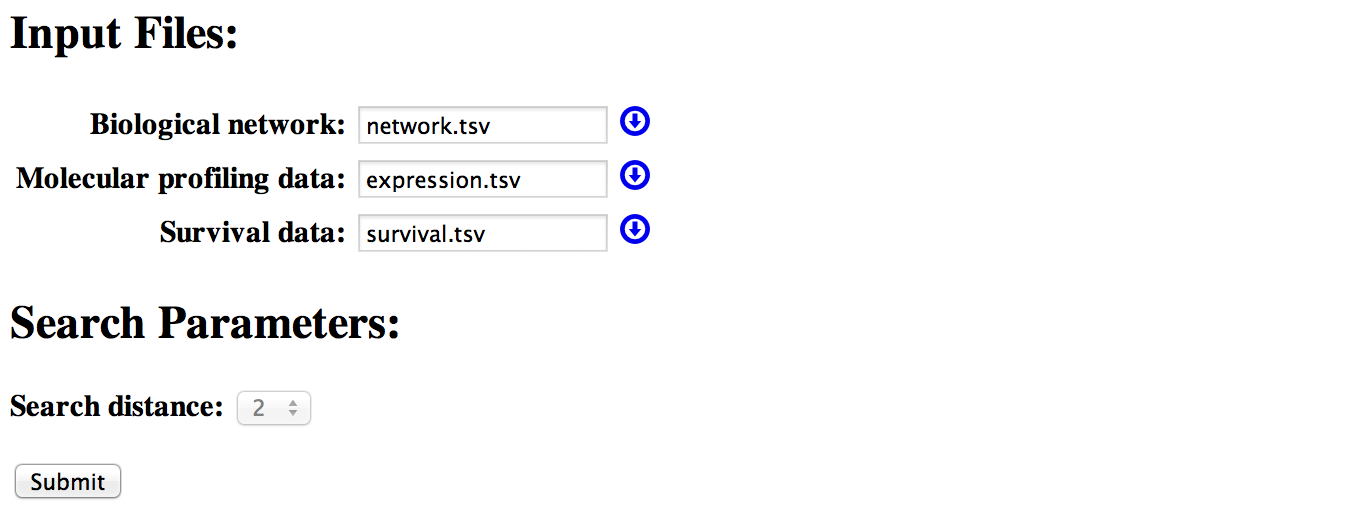
[top]Analyzing preloaded data
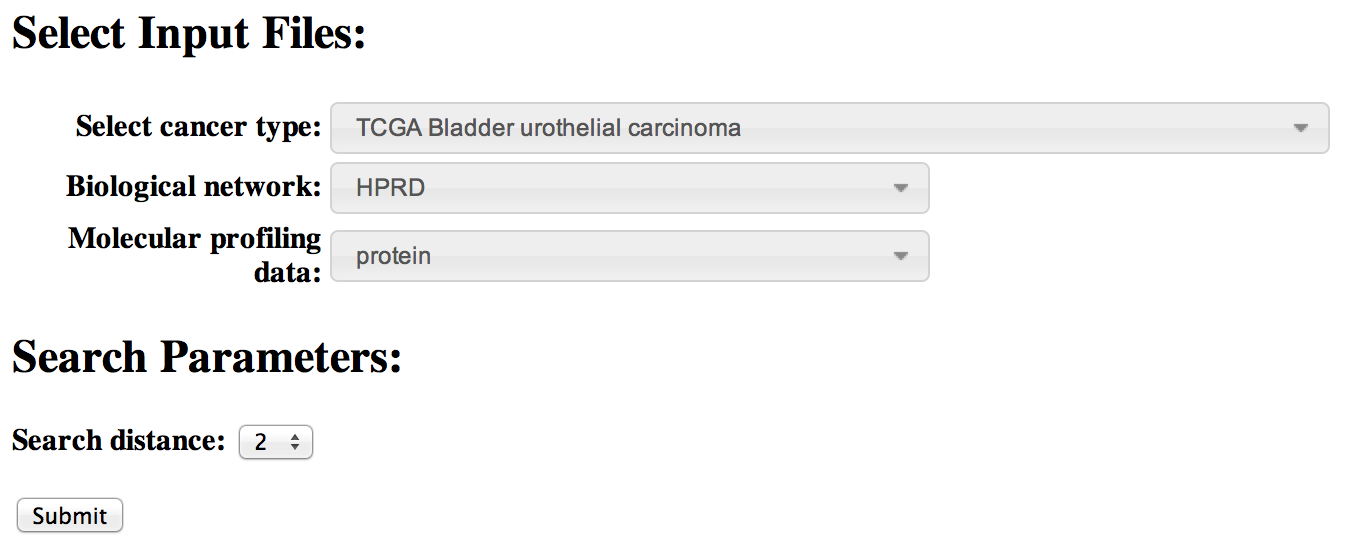
[top]To analyze preloaded data, you need to make a selection from each of the three pulldown menus.
Setting parameters
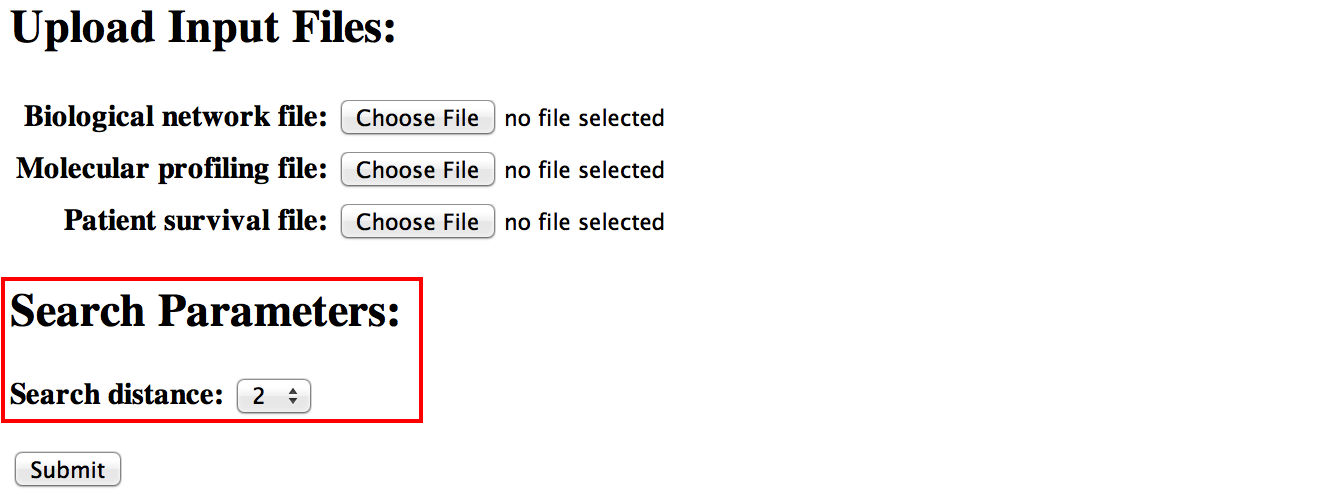
[top]You also need to specify a "searching distance" parameter. SurvNet will automatically start with each gene (or protein) node as the seed and search the optimal subnetworks within this distance. SurvNet uses the same network searching algorithm described in Chuang et al. (Molecular Systems Biology 2007;3:140) and Jia et al. (Bioinformatics 2011;27:1). The larger this parameter is, the longer the computation will take.
Submitting your job
[top]Once you upload/select the input files and specify the required parameters, click the button to run the job!
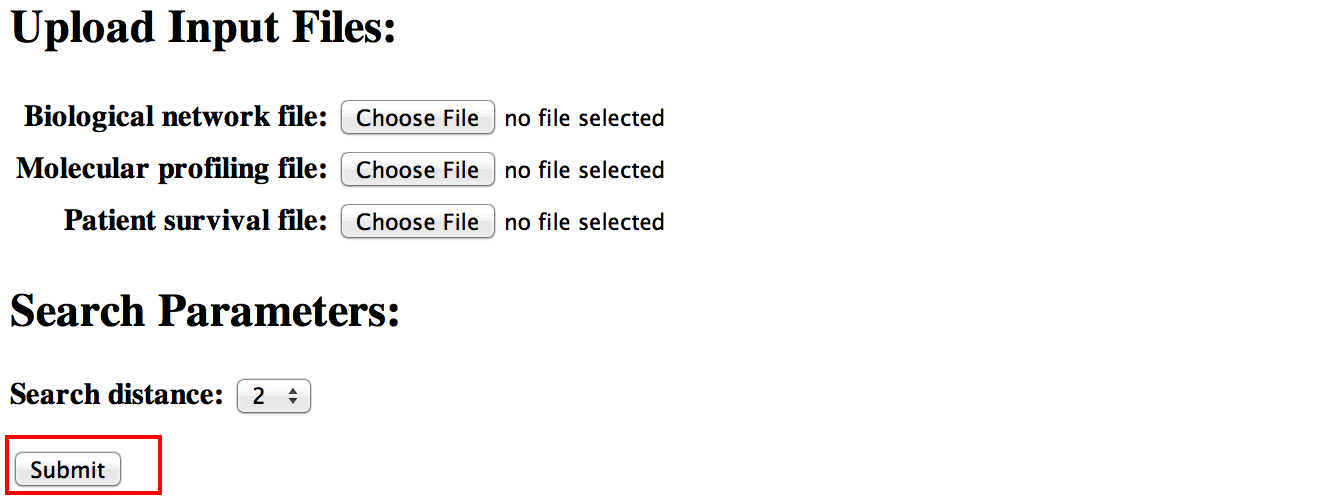
Demo
[top]Try out a set of sample data files (no user-provided input files are required).
Output
[top]- Summary page
After submitting a job, SurvNet will first check the data quality. If the input files are good, it will generate a data summary indicating the gene number, the sample number and so on.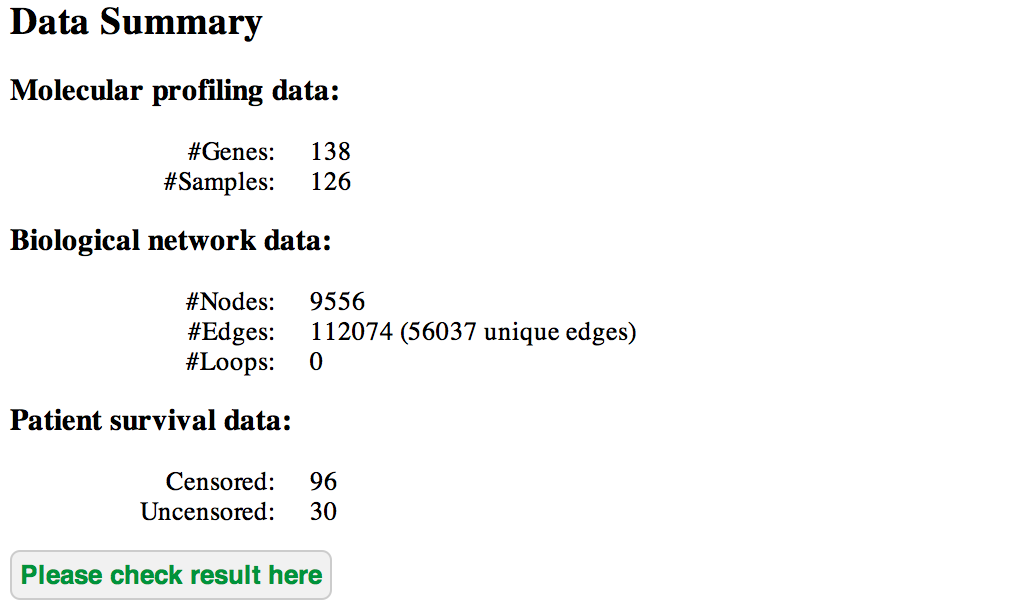
- Intermediate page
If the submitted job takes some time, an intermediate page will be generated indicating the job is still running. You can check the result by refreshing this page after a few minutes (see red box 1). Alternatively, the intermediate page also contains a weblink, and you can bookmark the link (see red box 2) and access the results later (the results will be maintained for two weeks).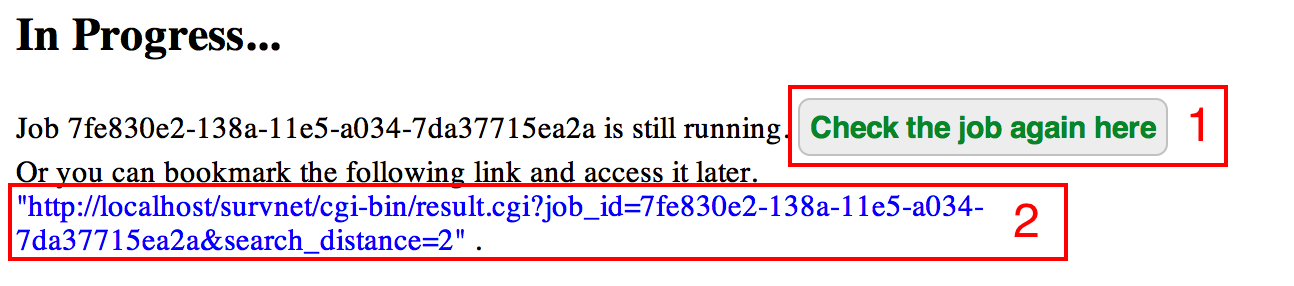
- Final output page
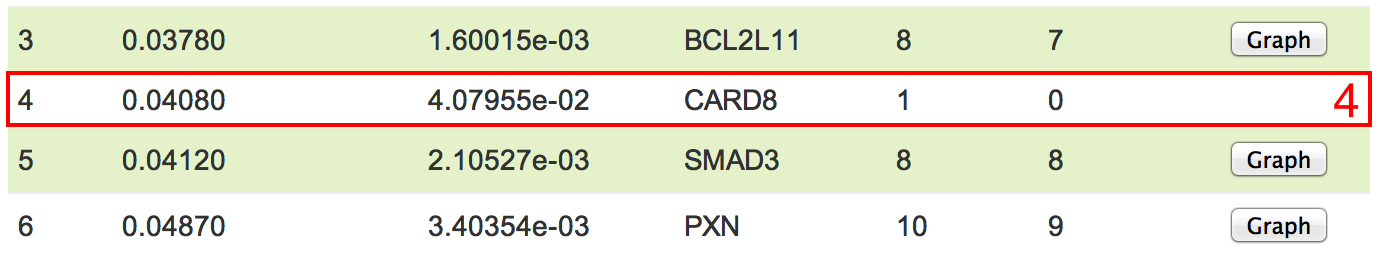
In the final output, you will see the results in the table format. You can download the table and the DOT format subnetwork file (see red box 1) which can be visualized by GraphViz. The identified top subnetworks rank with the network p-values (from low to high). The Network p-value is calculated based on the Cox proportional hazards model and network properties, which quantifies how significantly nodes in a sub-network correlate with the observed patient survival data. The higher the score is, the more significant the network correlates with the patients' survival. The Cox p-value is the p-value derived from multi-variable Cox proportional hazards regression model for evaluating the utility of subnetworks. The Gene ID indicates the seed node for each sub-network; the #Nodes indicates how many genes (or proteins) are in the network; the #Edges indicates how many interactions are in the network; and you can visualize the network by clicking the button (see red box 2). The identified subnetworks can be filtered by two parameters (see red box 3). There will be no button (see red box 4) if the sub-network is trivial (only including a single node).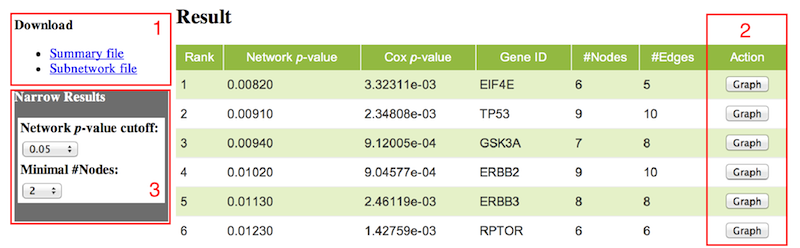
- Network visualization page
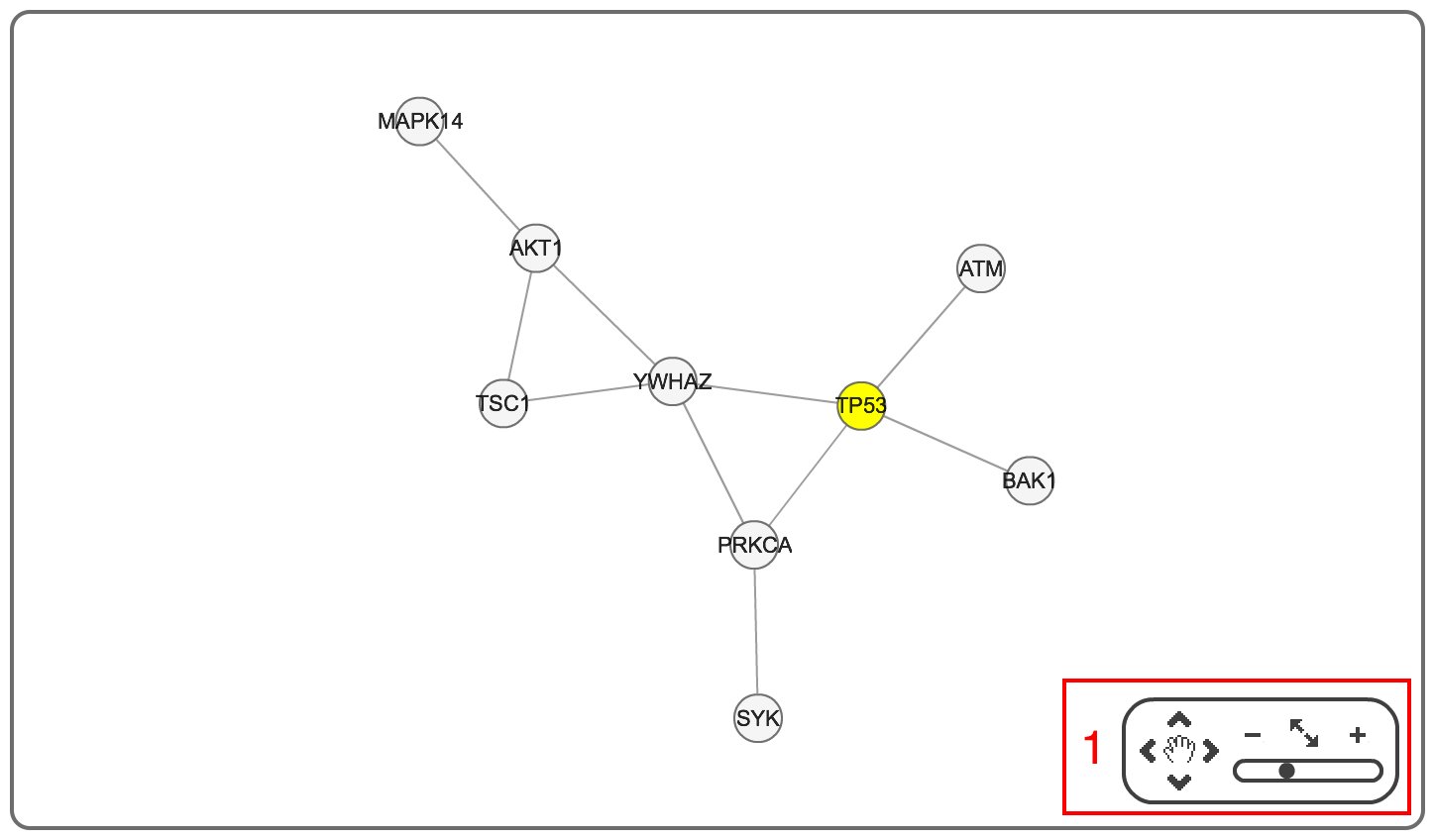
After clicking the button in the final output page, you can visualize a network graph in a user friendly interface (it may take a few seconds to load a network graph). Using the buttons in the red box 1, you can (i) adjust the location of a network; and (ii) zoom in/out of a network. You can go back to the final output page by clicking the button in the red box 2.